The brown hyenas, often overshadowed by the three other hyena cousins, are the rarest and least studied species in Africa. In the vast landscape of Africa, where predators like Lions, Leopard Wild dogs etc steal the spotlight, the species of hyena roams silently to confirm its survival in the heart of Kalahari.
Due to some unknown reason, the hyena species failed to gain the attention of wildlife enthusiasts, researchers and wildlife photographers. Today, we will delve into the world of brown hyenas and explore some secrets that will grow your interest in the species.
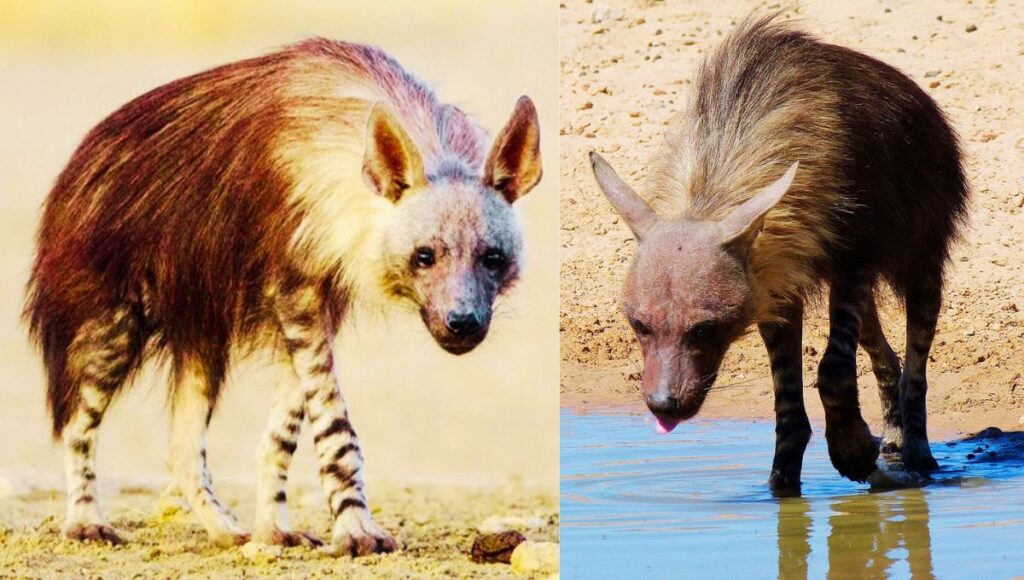

Table of Contents
The Brown Hyenas- In a Glimpse:
| Common Name: | Brown Hyena |
| Scientific Name: | Parahyaena brunnea |
| Group Name: | Cackle |
| Other Names: | Strandwolf |
| Infants Name: | Cub |
| Adult Weight: | 40-44 kg (Males) 37-40 kg (Females) |
| Adult Height: | 130-160 cm |
| Colour: | Brown |
| Speed: | 50 km/h |
| Bite Force: | 1100 psi |
| Distribution: | Angola, Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe. |
| Habitat: | rocky and mountain areas |
| Seasonal Behaviour: | Not a Migrant |
| Character: | Nocturnal |
| Diets: | Omnivorous |
| Predators: | African Lions and Spotted Hyenas |
| Family Size: | 4-6 |
| Threats: | Human false persecution |
| IUCN Status: | Near Threatened |
9 Interesting Facts about Brown Hyena:
Scientific Classification:
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Hyaenidae |
| Genus: | Parahyaena |
| Species: | Parahyaena brunnea |
Relatives:
| Relatives | Distribution | IUCN Status |
| Aardwolf | Africa | Least Concern |
| Spotted Hyenas | Africa | Least Concern |
| Striped Hyenas | Africa and Asia | Near Threatened |
Physical Description:

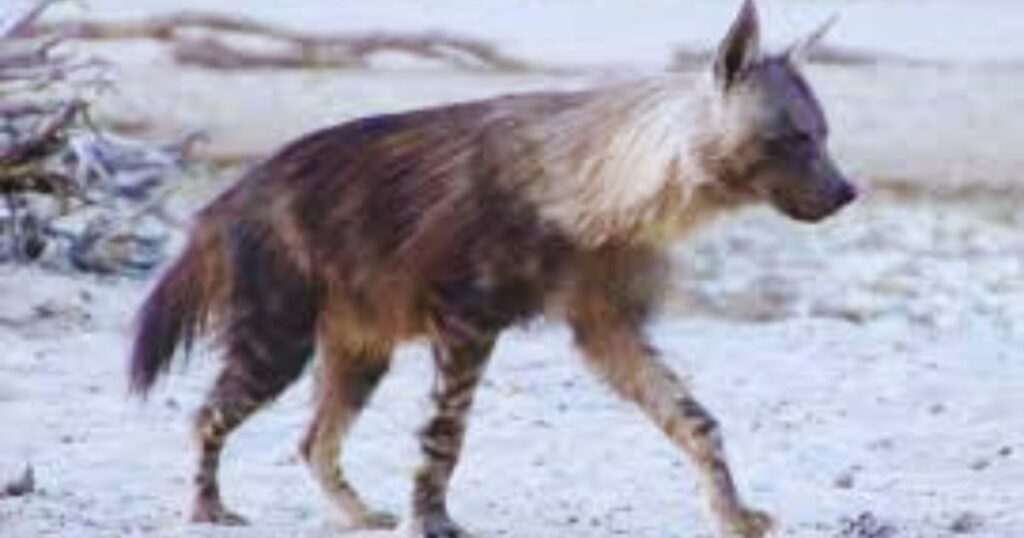
Unlike other hyena species, the brown hyena has a long shaggy dark brown coat, pointed ears, and a short tail. The colouration differs from pale brown to almost black. The legs are striped brown and white and adults have cream colour fur ruff around their necks.
The jaws are very powerful of the hyenas. A young brown hyena can crack the leg-bones of a springbok in just 5 minutes. Although this ability cripples with age due to dental wear and tear. The head skulls are larger than other hyena species and the dentition is robust.
Size:
The length of the body is 57 inches or 144 cm on average with a range of 130-160 cm. The shoulder height is 70-80 cm and the tail is about 21-35 cm long. Unlike their cousin spotted hyenas, the species doesn’t exhibit sexual dimorphism but the males are slightly larger than the female. The weight of an adult male is around 40-44 kgs whereas a female weighs 37-40 kgs.
Teeth:
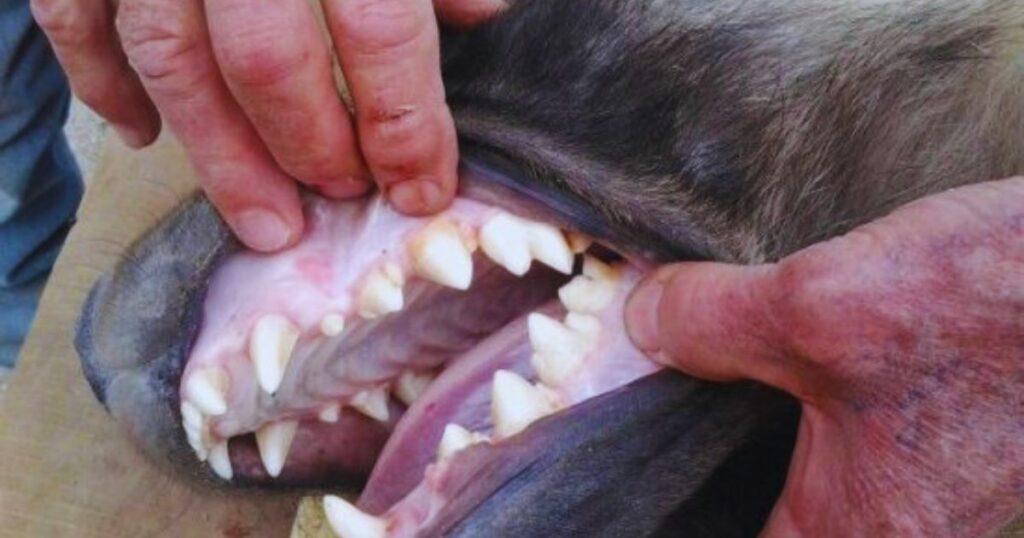
The teeth of brown hyenas are massive compared to other carnivores. The upper carnassial tooth is large and well-developed to crush the bones of the prey. The bite force of hyenas is 1100 psi which is 7th strongest among all animals. The hyenas usually have 32-34 teeth and the canine teeth are 5-6 mm long and the incisors are 4 mm long.
Distribution and Habitat:
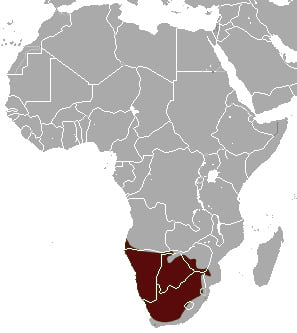
Once upon a time, the brown hyenas were found in the Iberian peninsula and other parts of Europe but now it is endemic to Southern Africa. It is mostly found in Angola, Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe.
The species lives in desert, semi-desert and open woodland savannahs. Being a scavenger, the hyenas can live close to the urban settlement as well. The species doesn’t require water resources for frequent drinking instead it prefers rocky and mountain areas as it provide shelter to the animal. The range of its territory is between 225 and 465 sq. km.
Behaviour:
Brown hyenas are primarily nocturnal as they spend 80% of their activity at night. For searching the food, the hyenas cover 30-35 km areas every night on average. They store the excess food in shrubs or holes and finish it within a day.
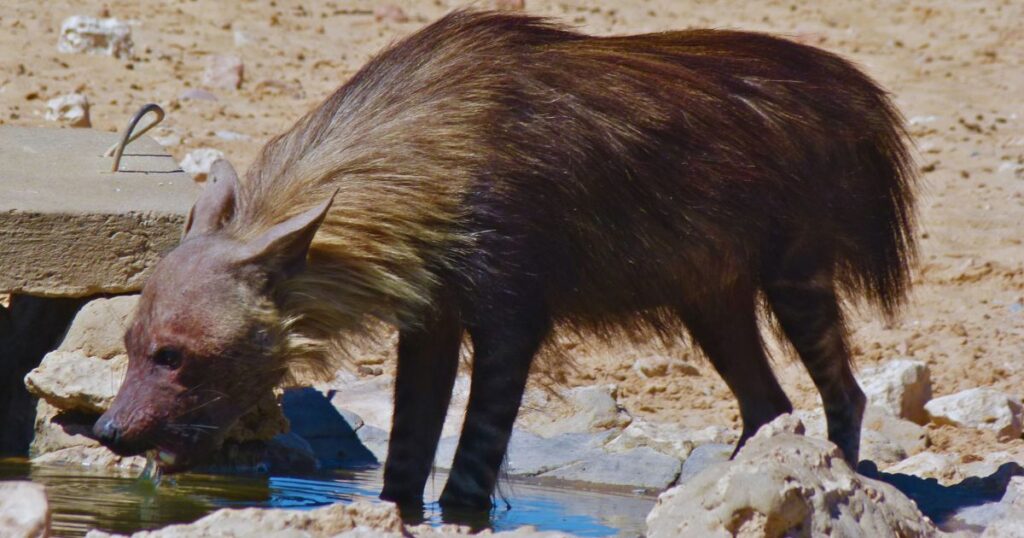

The social structure is comparable to the wolf, consisting of a couple and the offspring. The size of the family/clan is generally from four to six individuals. The clan defends the territory which is marked by ‘Pasting’ ( a substance that secretes from the hyena’s anal gland). All members of the family help in raising their infants, also known as cubs.
Brown hyenas maintain a stable clan hierarchy through aggressive displays and mock fights. A male hyena can move up in the social structure only by killing and replacing a higher-ranked male hyena in confrontation. The oldest female of the clan is usually the alpha female of the family. Young males can join another clan after reaching adulthood.
Communication:
Brown hyena has a good smelling sense which helps them to communicate valuable information among clan members without physical interaction. Hyenas have two types anal secretion:

- The Black Paste: the odor of the paste fades quickly and it conveys the message to the clan members that the area has been searched for food.
- The White Paste: the odour lasts for 30 days and it expresses the territorial boundary of the clans.
This marking exists all over the territory but it is more frequent towards the boundaries. Defection scents are also used to convey messages about what they have recently eaten and the scent is more prominent near the dens and boundaries.
The hyenas also produce visual displays to communicate in addition to scents marking.
- If the tail is laid against the back, the ears are alert and the mouth is closed, indicating an aggressive situation; and
- Defensive displays are characterized by an open mouth and flattened ears.
Diets:
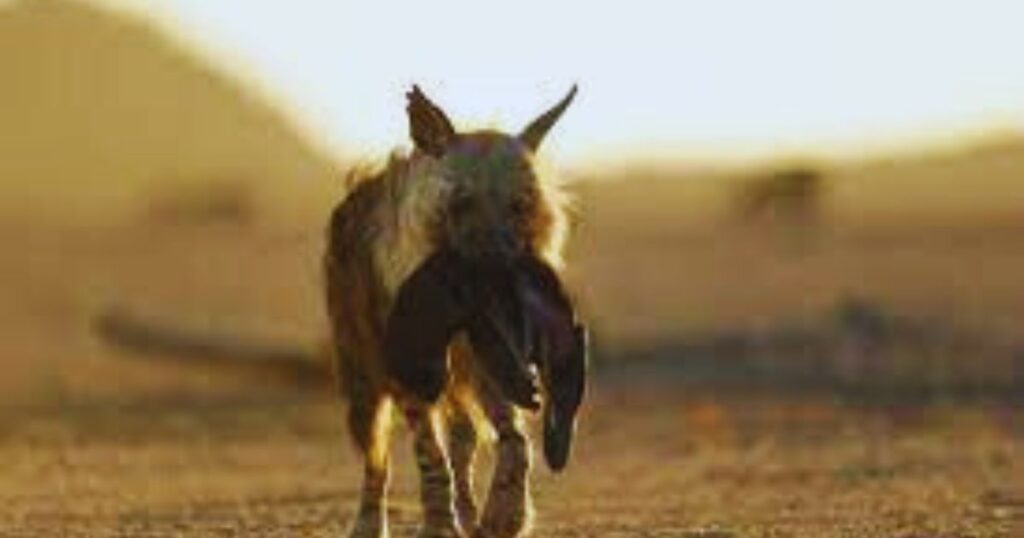

The brown hyenas are poor hunters and thus they are primarily categorised as scavengers. Its diet mainly consists of carcasses killed by larger predators (lions, cheetahs or leopards). They also supplement their diet with rodents, insects, eggs, fruit and fungi. The species also feeds on ostrich eggs and even desert melons. Hunting consists only 2.5-4.5% of their overall diets.
The hyena species has an excellent sense of smell and they can locate carcasses kilometres away.
The brown hyenas are excellent kleptoparasites. In other words, they can snatch food from other animals very aggressively. A single hyena can fight for food and win over a leopard due to its strong jaw. Thus, in the Kalahari desert, they are dominant carnivorous in the absence of enough lions, spotted hyenas and packs of wild dogs. Although, where the territories overlap, the hyena species are killed by spotted hyenas and lions.
Ecological Importance:
Brown hyenas are very important for humans and the environment:
- They can be beneficial as the main attraction of eco-tourism, which brings more money and create more jobs in the region.
- By reducing the number of carcasses, the hyenas control parasites that rely on animal carcasses to feed and reproduce. It also reduces parasitic infection in humans, livestock and domestic pets.
Reproduction:
| Mating Season: | May-August |
| Breeding Interval: | 20 months |
| Gestation Period: | 97 days |
| Litter Size: | 1-5 |
| Infant Weight: | 1 kg |
| Weaned at: | 12 months |
| Age of Independence: | 18 months |
| Sexual Maturity of Males: | 30 months |
| Sexual Maturity of Females: | 24 months |
| Lifespan: | 12-15 years |
Unlike other African species, brown hyenas don’t have a breeding season. The females are polyestrous and produce their first litter at two years old. They generally mate between May and August. Females don’t mate with males of the same clan instead they mate with nomadic males. The males of the clans show no resistance while mating and help the female to raise the cubs.
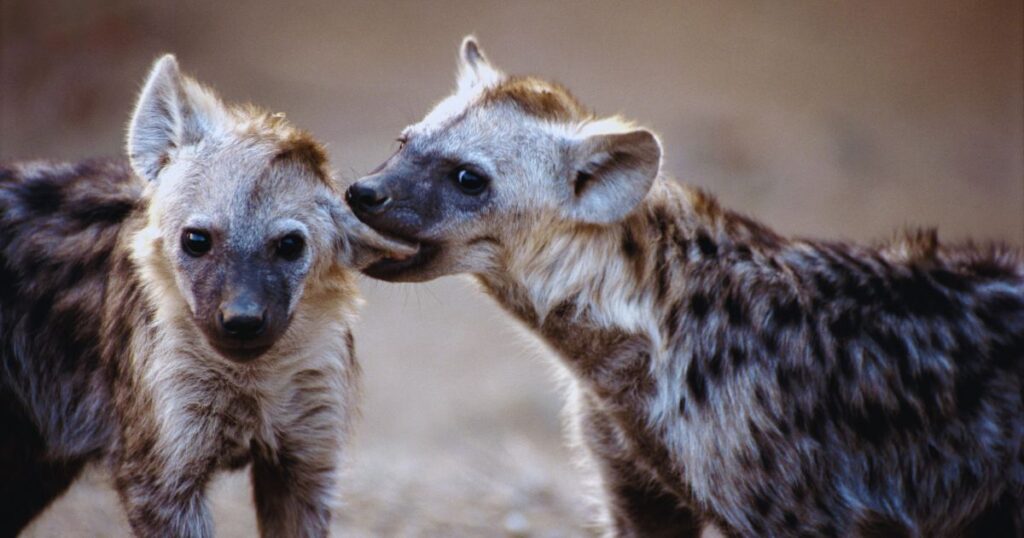

Females give birth to the cubs in dens which are in remote sand dunes, far from spotted hyenas and lions. The average gestation period is 97 days and females produce 1 litter every 20 months. If two different mothers give birth to two litters within the same clan, then mothers will nurture each other cubs, favouring their own.
The litter usually consists of 1-5 cubs which weigh around 1 kg or 2.2 lbs during birth and their eyes are closed, unlike spotted hyenas. The cub open their eyes after 8 days and weaned at 12 months and leave the dens after 18 months. All the adult members carry food to the cubs and the hyenas reach their full size at the age of 30 months.
Lifespan:
The hyenas generally live 12-15 years in the wild.
Predators:
African lions are the main predators of brown hyenas. Although spotted hyenas also kill the species only in the confrontation between the two which occurs rarely due to different habitat preferences. The cubs are vulnerable to lions, black-backed jackals and African wild dogs.
Threats:
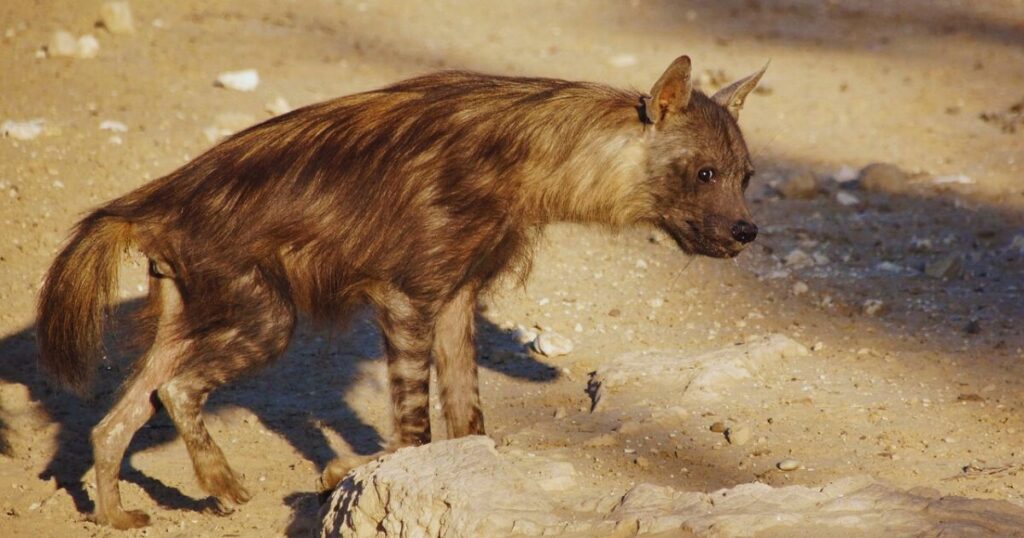

The major threats to brown hyenas are false human persecution as they are harmful to the livestock. The farmers found that the hyenas scavenged on livestock carcasses but failed to assume that the livestock are killed by bigger predators. The body parts are used occasionally for traditional medicine and rituals.
IUCN Status:
The current population of brown hyenas are estimated between 4000 and 10000. It is listed as Near Threatened in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The species is not listed in CITES but is considered Endangered in the US Federal List.
Conservation Efforts:
The maintenance and preservation of the conservation areas such as Etosha National Park in Namibia, the Central Kalahari Game Reserve in Botswana and the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, Educating the locals about the animal and destroying the myth that brown hyenas are good hunters are few of the steps that were taken from Governments and NGOs.
Best Places to Watch Brown Hyenas:
You can watch the species in Central Kalahari Game Reserve (Botswana), the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park (Botswana/South Africa) and the coastal and northern desert regions of Namibia, Madikwe and Pilanesberg reserves in South Africa.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How many brown hyenas are left in the world?
Unfortunately, there are only 4000-10,000 populations of the species left in the Southern Part of Africa. It is listed as Near Threatened in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Is a brown hyena bigger than a spotted hyena?
No, while confrontation between the two types of hyenas, the spotted hyena often kills the other one. A spotted hyena weighs around 40-64 kg. Its length is around 100-165 cm and its height is 70-90 cm.
Whereas the brown hyena weighs around 37-44 kgs, 130-160 cm in length and heights around 70-80 cm. Hence, the spotted hyena is bigger and more powerful.
Are brown hyenas aggressive?
Well, the hyenas are not good hunters but they are very aggressive kleptoparasites or masters at snatching food from other animals. A single brown hyena can even defeat and tree an adult male leopard.
What animals did hyenas evolve from?
Although hyenas look like dogs, they are closer to cats. The hyenas evolved from the Cat group. Order Carnivora was split into cat and dog 50 million years ago. The Hyaenidae family evolved from cat groups around 30 million years ago.
What is the rare breed of hyenas?
There are four types of hyenas around the world. Among them, the brown hyenas are less studied and also rarest among all. Only 4000-10,000 populations are left of the species.
What is a hyena’s worst enemy?
Lions are the worst enemy of Hyenas. They often fight over food. Although, Lions often kill hyenas the bite force of hyenas (1100 psi) is almost double that of Lions (625-650 psi).
Do hyenas harm humans?
Usually, Aardwolf and Brown hyenas don’t harm humans. But Spotted hyenas are very aggressive, dangerous and of predatory nature. They often attack children, women and frail persons but rarely attack healthy men.
Do hyenas like being pets?
An adult hyena is wild and aggressive in nature. Being a predatory animal, they are not suitable as pets. They may harm other domestic pets due to their wild and predatory nature. But a young hyena loves human company and belly rubs.
What is the most aggressive type of hyenas?
Out of the four types of hyenas, spotted hyenas are the largest, strongest, biggest and most aggressive type of hyenas in the world.