A Swift Fox is a very fascinating and elusive creature that mostly lives in the grasslands of North America. It is one of the smallest members of the Canidae family. This charismatic fox species has earned its name due to its agile and swift movements in the grassland.
Endemic to the Great Plains or Prairies, the animal gained spaces in the heart of wildlife enthusiasts and photographers. In this dedicated article about Swift Fox, we will delve into every detail and discuss why this animal is so important to the ecosystem.
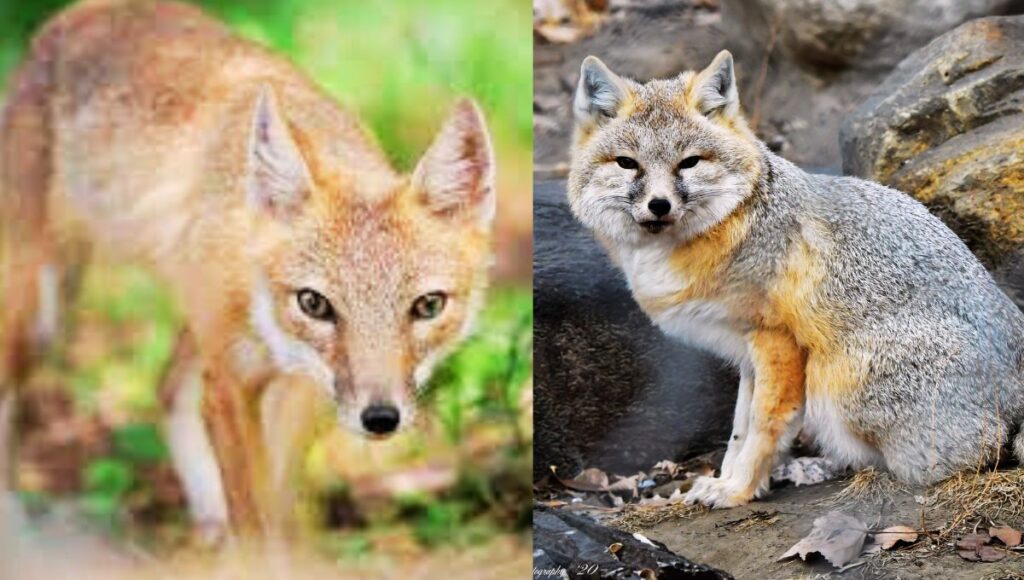

Table of Contents
The Swift Fox- In a Glimpse:
| Common Name: | Swift Fox |
| Scientific Name: | Vulpes velox |
| Group Name: | leash, skulk, earth, lead, troop |
| Adult Weight: | 2-3 kgs |
| Adult Height: | 12-16 inches |
| Colour: | golden to yellowish brown |
| Speed: | up to 60 Kmph |
| Distribution: | from Southern Canada to Southern parts of the USA |
| Habitat: | grassland, prairies, and shrub-steppe region |
| Seasonal Behaviour: | Not a Migrant |
| Character: | Cursorial, usually Monogamous but some of them change partners every year. |
| Diets: | Omnivorous |
| Predators: | Coyotes, badgers, golden eagles and bobcats. |
| Life Span: | 3-6 years in wild but up to 14 years in captivity. |
| Family Structure: | Matriarchial |
| Threats: | Trapping, Poaching, Road Accidents |
| IUCN Status: | Least Concern |
| Infants Name: | kit, cub, pup. |
Everything About Swift Fox:
Scientific classification:
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Vulpes |
| Species: | Vulpes velox |
Physical Characteristics of Swift Fox:

The Swift Fox is a very petite and agile animal, weighing around 2-3 kg or between 4 and 7 lbs. Its height is about 12-16 inches and its length is approximately 30-35 inches. The male and female don’t show dimorphism in appearance but the male is slightly larger.
It has a golden to yellowish brown coat with a white to pale yellow underbelly and black-tipped ears. The unique colouration helps them to hide in the natural grassland from potential threats and predators like coyotes, eagles and larger carnivores.
The slender and elongated body with short legs enhances their agility to move around the grasslands at a very high speed as much as 60-65 kmph. Strong senses, acute hearing and sharp eyesight play important roles in locating prey and finding potential threats.
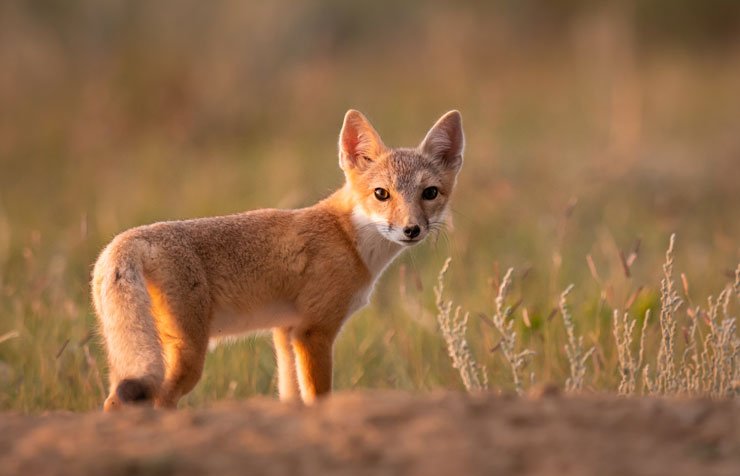
Distribution or Habitat:
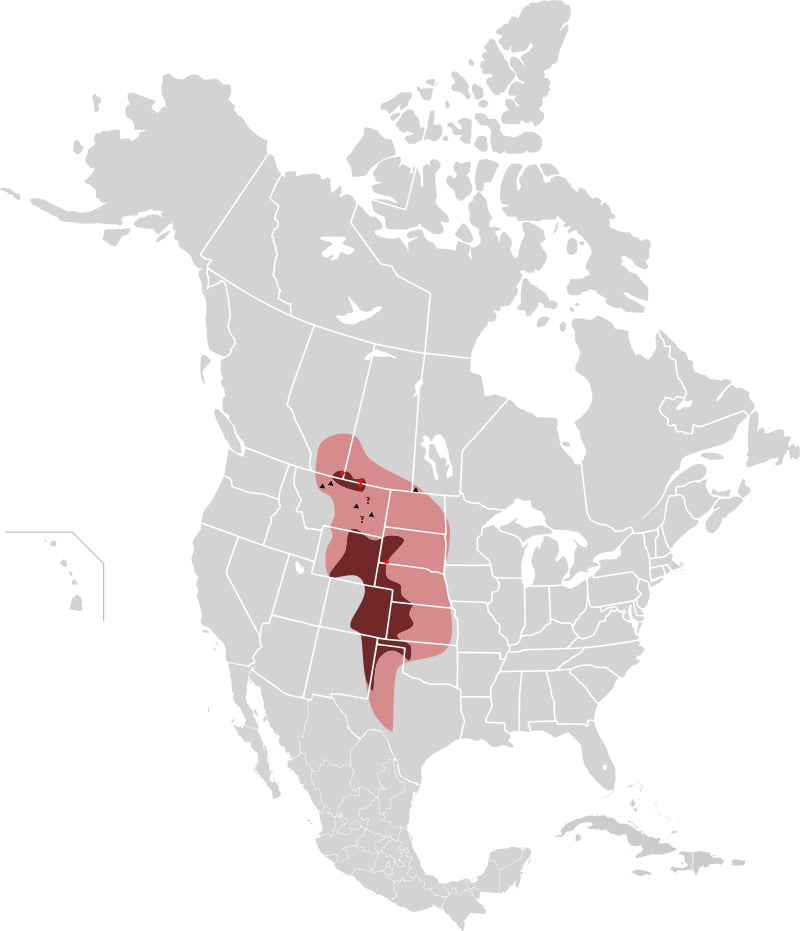
Previously, the habitats of Swift foxes were across the entire Great Plains region in North America, from Southern Canada to Southern parts of the USA, including southern Alberta, Saskatchewan, Colorado, Kansas, Wyoming, Nebraska, and Montana. However, due to habitat loss and human encroachment, their distribution range is squeezing significantly.
Swift foxes are endemic to the Great Plain region and generally prefer vast grassland, prairies, and shrub-steppe regions where the animal finds sufficient cover of protection and dens.
The colour of the furs helps them to protect themselves from predators. They also love to inhabit agricultural lands and pastures where they find enormous supplies of food such as rodents.
Behaviour and Habits:
Swift foxes are primarily nocturnal animals. Their activities are heightened at dusk and dawn. They generally spend only evening and nighttime above the grounds during summer. They are generally confined to their burrow/den during sunlight but in the winter season, they often enjoy sunlight above ground.
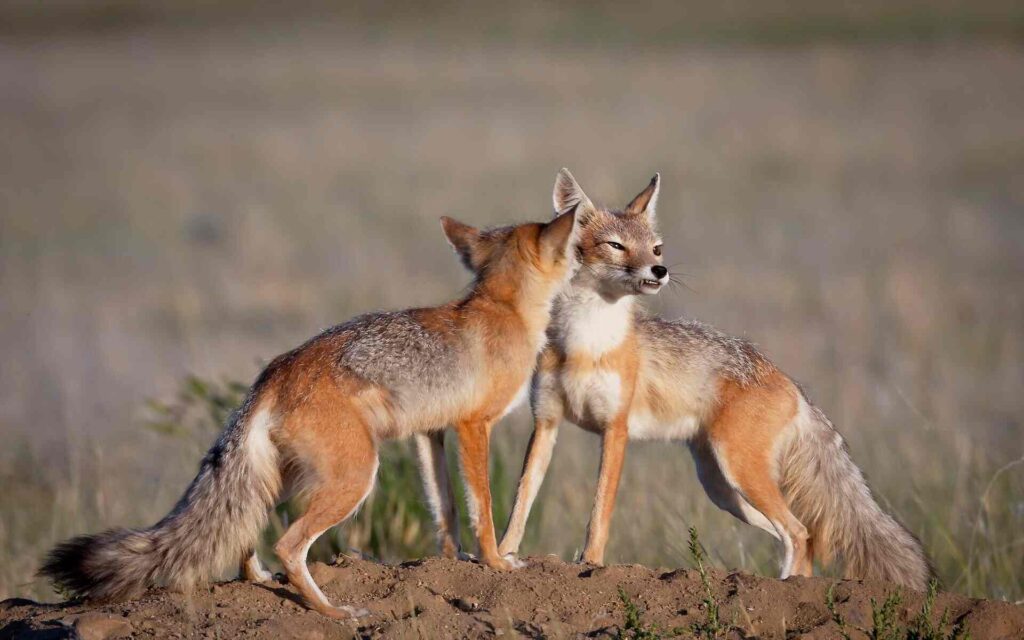

The mortality rate of Swift foxes is increasing day by day due to the harsh winter conditions in the region. Their dens are usually a burrow which is 2-4 meters long, which not only helps them to get protection from predators but also from the cold weather.
Swift foxes are cursorial animals which is adapted to run very fast up to 60-65 Kmph to escape from their predators such as coyotes, badgers, golden eagles and bobcats. Swift foxes are also very vulnerable to trapping and poisoning due to their valuable furs and face road accidents on highways often.
Swift foxes are known as scavengers of the Prairies as they have been often observed to scavenge on carrions and clean the environment. Swift foxes are an indicator of a compact grassland ecosystem. Their presence benefits other animals that share similar ecosystems such as prairie dogs, ground squirrels, and grassland birds.
Diets and Nutritions:
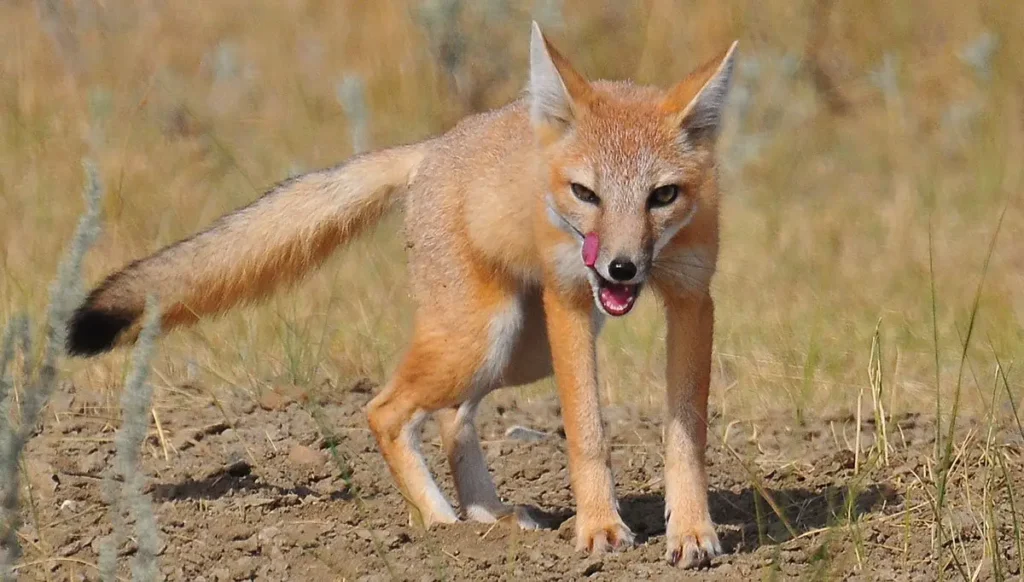

Like most foxes, Swift foxes are omnivorous, but their diets change seasonally depending on what is available to eat. Rabbits, mice, ground squirrels, birds, insects, eggs and fish are their main staples. Grasses and fruits are also very important parts of their diets. The average basal metabolic rate is 4.9W for an adult fox.
Being very adaptable and opportunistic by nature, Swift foxes also take advantage of seasonal foods. During summer they consume a lot of beetles and grasshoppers in their diets. Deer and other carrion were killed by large carnivorous are also they important food source.
Reproduction:
| Mating Behaviour: | Monogamous but some of them change partners every year. |
| Breeding Season: | Differs but mostly December to February. |
| Breeding Interval: | 1 year. |
| Gestation Period: | 51 days |
| Litter Size: | 3-6 |
| Independent Age: | 6 months |
| Sexual Maturity of Males: | 1 year |
| Sexual Maturity of Females: | 2 year |
| Weaning Age: | 42-49 days |
Swift foxes show monogamous characters in relationships. Multiple breeding strategies are observed and breeding season differs with regions. In southern USA, the pair meets usually between December and February and the pups are born in March-April. But in Canada, the breeding season begins in March and the pups are born at the end of May or beginning of June.
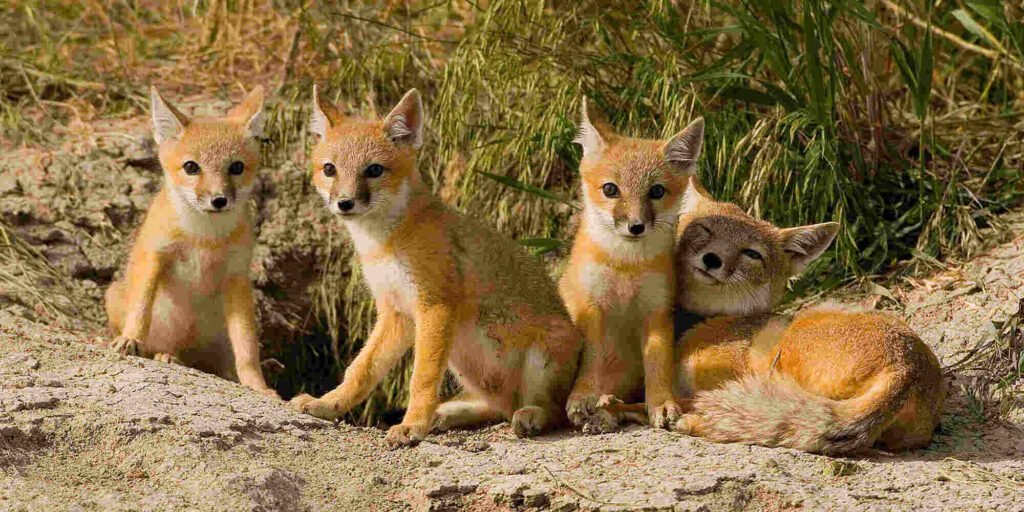

Adults usually live in pairs. Mostly they are monogamous by nature but some of them choose different partners each year. Their gestation periods are usually 51 days and the litter size is 3-6. The pups are born blind (for 10-15 days) and entirely depend on the parent foxes for food. The couple takes care and nurtures the young foxes and performs parental responsibility and protects them from predators.
The social structure of the swift fox is uncommon among other canids as it is based on a matriarchal society. The females maintain and protect the territory all the time and the male emigrates if the residing female is killed or removed.
Life Span:
The life span of Swift fox is usually 3-6 years in the wild but may live up to as high as 14 years in captivity. It is shown in studies that the average life span is around 12 years in captivity.
Main Predators:
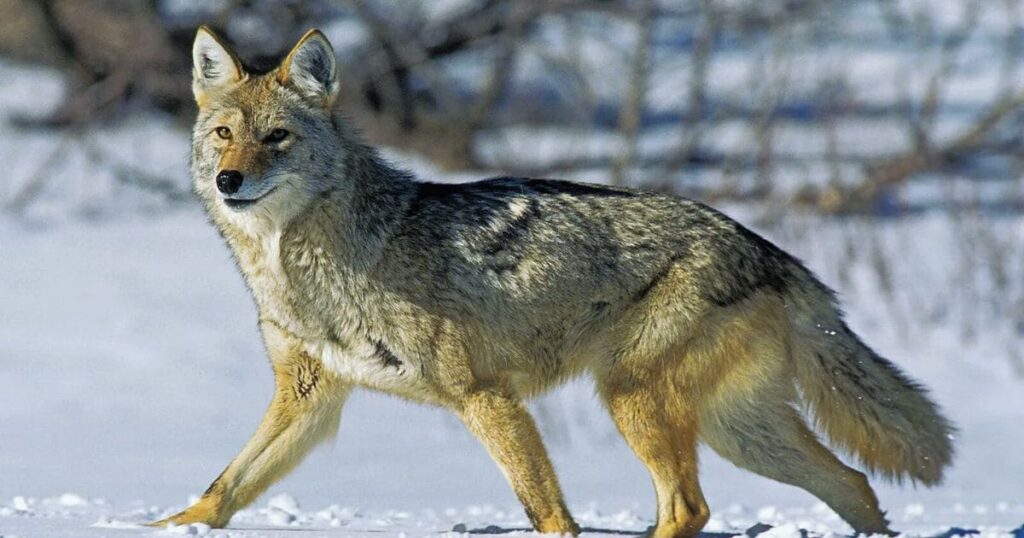

Larger carnivores in the region are their main predators. Coyotes are the main predator of Swift foxes but badgers, golden eagles and bobcats are also on the list. Coyotes although kill Swift foxes and often choose not to consume them.
Other Threats:
Swift foxes face many anthropogenic threats as well. In the 1930s, they were nearly extinct because of predator control programs and in 1938, they were considered as extirpated from Canada. But in 1983 the reintroduce program started and was implemented successfully.
The fur of Swift Fox is very valuable. Thus the fox species is very vulnerable to trapping and poaching. With the expansion of agricultural land, urbanization and proliferation of roads, the habitats of Swift foxes are squeezed and they often meet road accidents on highways.
Conservation Status:
| IUCN Status: | Least Concern |
| CITES: | No Special Status |
| US FEDERAL LIST: | Endangered |
The fox species are recorded as ‘Least Concern’ in the IUCN Red List of threatened species. But they have no special status in CITES.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Why did the Swift Fox become extinct?
In the 1930s, Swift foxes were nearly extinct due to the Predator Control Program. The program was launched to protect livestock and domestic animals from predators. Coyotes, bobcats, grey and red wolves, bears, and mountain lions were the main targets but unfortunately, the small foxes were also affected in this process. Later swift foxes were reintroduced in the region successfully and now they are listed as the Least Concern species in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Why do the swift foxes matter?
Swift foxes are an important indicator of intact grassland. The presence of Swift foxes indicates the health of the grassland and the food chain. Conserving habitats for the foxes also helps the other animals that share a similar ecosystem as prairie dogs, ground squirrels, and grassland birds. Swift fox also lives in agricultural land and pastures consume rodents as food and help the locality to stay away from disease.
Is the Swift fox a prey or predator?
Swift foxes are known as opportunistic predators as they consume the leftover carrion and scavenge the environment. But in reality, they are secondary consumers in food chains. The foxes consume rabbits, mice, and insects as their food and larger predators like coyotes, badgers, golden eagles and bobcats often hunt the small fox species. So, we can assume, They are Prey as well as an Opportunistic Predator.
Is Swift Fox Protected?
No, Currently Swift foxes are not protected. In 2001, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service removed it from protection as the recovery program was successful. But in the US Federal List it is still in the Endangered category. Although, IUCN consider it as a Least Concern species.
What is the difference between a Swift fox and a Gray fox?
Grey foxes are almost double in size as a Swift fox. Swift foxes weigh around 2-3 kg but Gray foxes are heavier from 4-7 kg. Swift foxes live a maximum of 6 years in the wild but Gray foxes live longer (around 8-9 years). Swift foxes (60 Kmph) are faster than Gray foxes (45 Kmph). The fur of grey foxes is usually a mix of white, red, grey, and black whereas swift foxes are usually grey to yellowish in colour.
What is the difference between a Swiftfox and a Kitfox?
Kit foxes are smaller compared to Swift foxes. The length of Kit foxes is usually 455-535 mm and Swift foxes are about 79 cm. Swift foxes are omnivores whereas kit foxes are usually carnivores. Kit foxes have longer ears of about 2.8-3.7 inches whereas Swift foxes have comparatively smaller ears. An average adult kit fox weighs between 1.5-2.7 kg whereas a swift fox weighs between 2-3 kg. Swift fox has a unique family structure in the Canidae family. Swift fox has a matriarchial family structure whereas kit foxes have a patriarchial structure.
Governmental and Non-Governmental agencies have implemented different strategies and formulas to safeguard the captivating, agile and attractive fox species. These strategies include habitat restoration, generating public awareness and establishing protected areas to preserve them at their natural habitat. We must ensure the survival of the Swift Foxes in the Prairies as it indicates the intact grasslands and rich biodiversity of North America.