The plateau pika, also known as the black-lipped pika, is a small mammal belonging to the order Lagomorpha, and has captured all attention of wildlife enthusiasts and photographers around the world. In this article, we will delve into the world of plateau pika and find out the fascinating characteristics and adaptability shown by the small mammal.
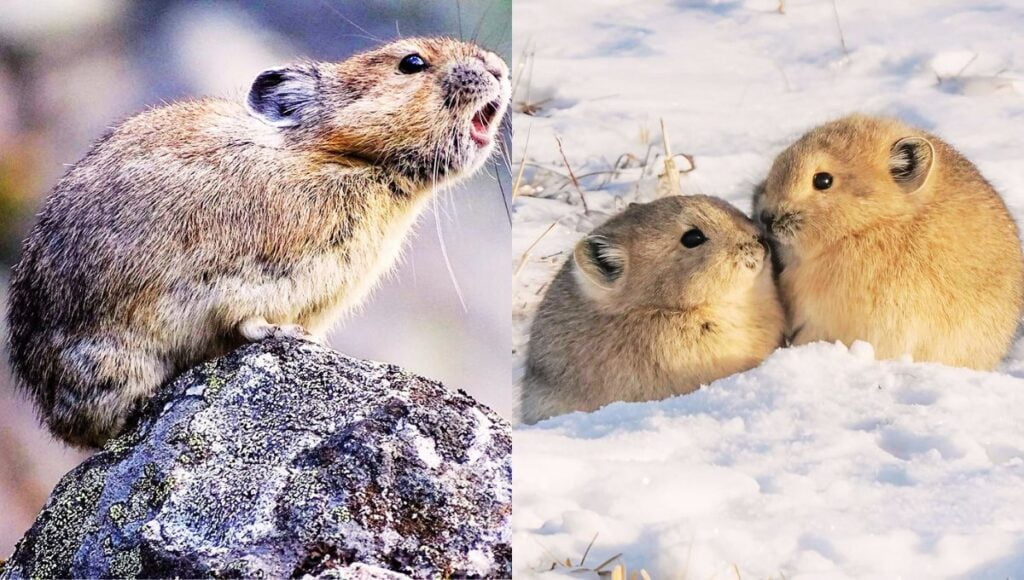

Table of Contents
Plateau Pika- In a Glimpse:
| Common Name: | Plateau Pika |
| Scientific Name: | Ochotona curzoniae |
| Group Name: | Colonies |
| Other Names: | Black-Lipped Pika |
| Fur Colour: | Brown to Red |
| Adult Weight: | 130-150 grams |
| Sexual Dimorphism: | Doesn’t show |
| Lifespan: | 490-500 days |
| Distribution: | China, India, Nepal and Bhutan. |
| Habitat: | High alpine deserts, steppes and meadows, and tropical and sub-tropical montane forests. |
| Lives in: | Burrows |
| Social Structure: | Foxes, weasels, falcons, Asia pole cats, and brown bears. |
| Diets: | Herbivore |
| Sexual Orientation: | Monogamous and polynandrous, |
| Breeding Season: | April-August |
| Breeding Interval: | 3 Week |
| Litter Size: | 2-7 |
| Age of Independence: | 1 Year |
| Predators: | Foxes, weasels, falcons, Asia pole cats, brown bears. |
| IUCN Status: | Least Concern |
7 Facts About Plateau Pika:
Scientific Classification:
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Lagomorpha |
| Family: | Ochotonidae |
| Genus: | Ochotona |
| Species: | Ochotona curzoniae |
Physical Description:
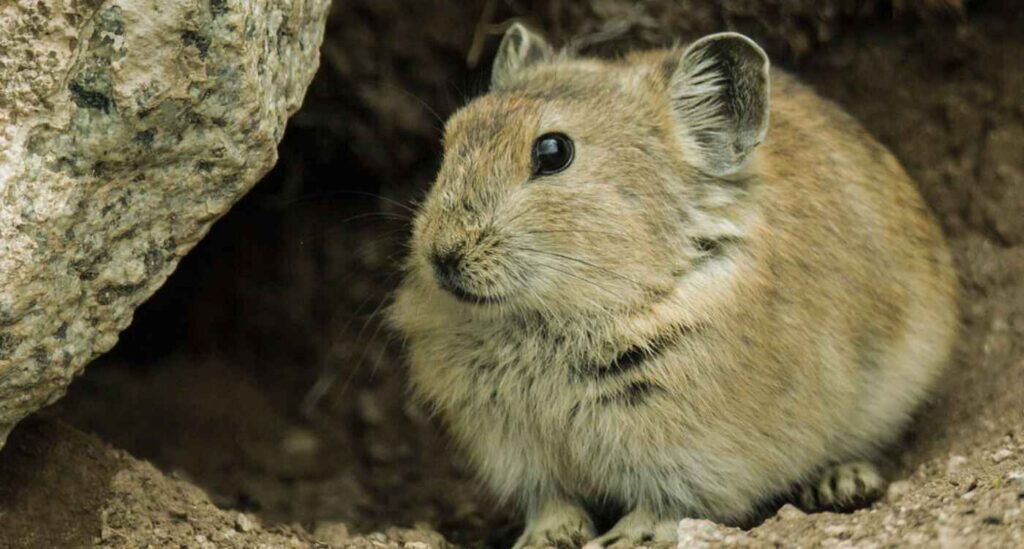

Plateau pikas are small and oval-shaped mammals having black lips. The colour of their thick fur varies from brown to reddish tan on the dorsal and whitish yellow on the underbelly. The species doesn’t show sexual dimorphism. The adult pikas weigh between 130-150 grams and they are a diurnal and non-hibernating mammal.
Lifespan:
The pikas have a lifespan of more than 1 year due to harsh winters and high parasitosis. Only around 2% of pikas can survive till the third year. The average lifespan of the pikas is between 490 and 500 days.
Distribution and Habitats:
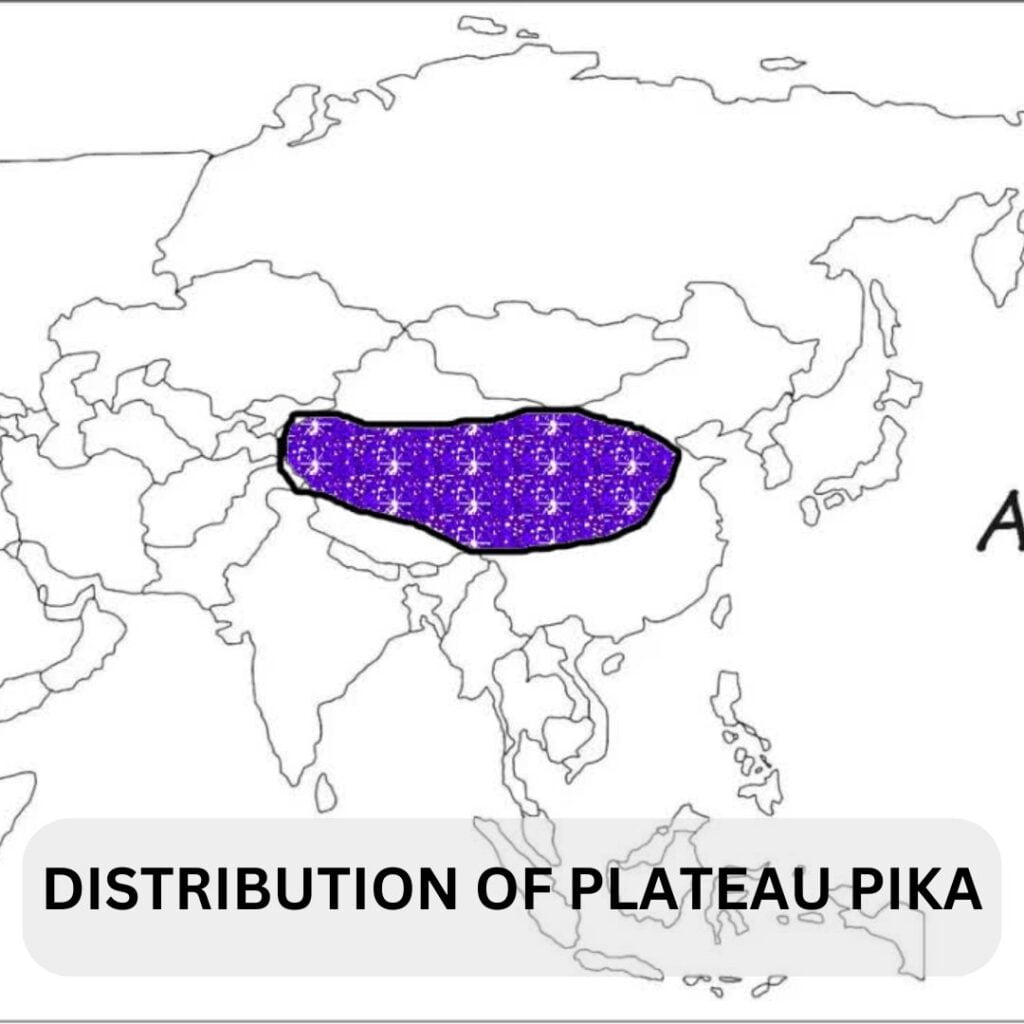
The pikas love to live in elevations of 3,100 -5,000 m in the Tibetian plateau. China, India, Nepal and Bhutan are the home of the little pikas.
High alpine deserts, steppes and meadows, and tropical and sub-tropical montane forests are the preferred landscape for plateau pikas. The home of pikas are burrowed which are built in flat to gently sloping terrain and silty to sandy soiled meadow land.
Behaviour and Social Structure:
The pika families consist of one male, one female and 5-10 juveniles. The family lives in burrows having multiple entrances and exits which help them to escape from predators.
Pikas are more cohesive in the meadowlands than in the plateau desert because of the abundance of food in the meadowland. The pikas are territorial and males chase off the members of other families.
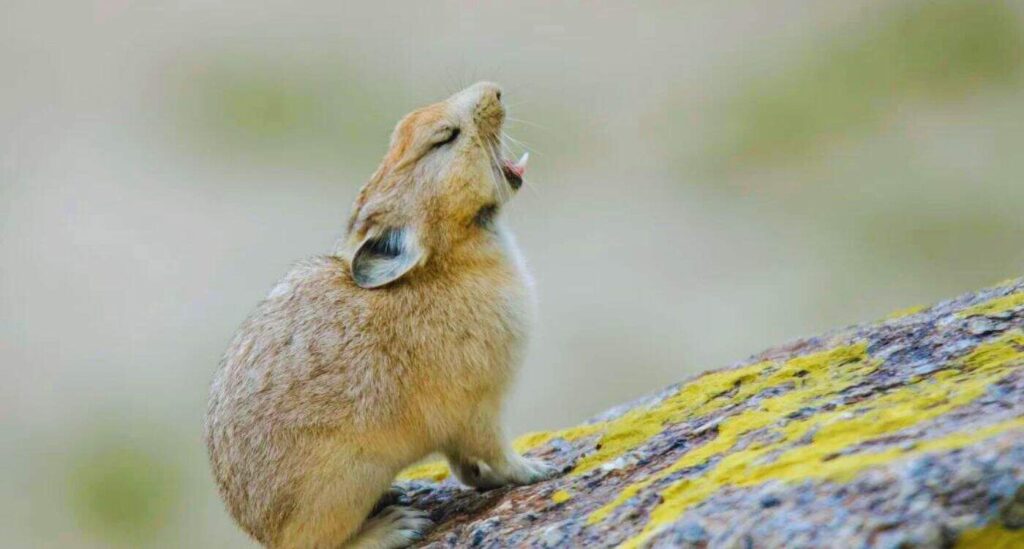

The males protect the burrow and teach the juveniles about gestures and self-defence and the females forage for food and groom children. Pikas don’t hibernate even in harsh winter and their activity begins with sunlight and continues till sunset.
Communication:
The pikas communicate with family members with various gestures such as grooming, and boxing and even they use vocal sounds to inform members about potential threats.
Diets:
The plateau pikas spend their most time foraging for food. The pikas that live in meadowlands usually have greater availability of food than those that live in desert plateau regions. The pikas are primarily herbivores. They usually feed on leaves, grains, seeds, flowers and plants.
Reproduction:
Plateau pikas have various types of mating systems such as monogamous and polynandrous, which include 3-4 males and females per family along with their offspring. When one adult pika dies, his family joins another group and promiscuity is common. The litter size produced by female pikas is generally between 2 and 7 and there is a 3-week interval between each litter produced.
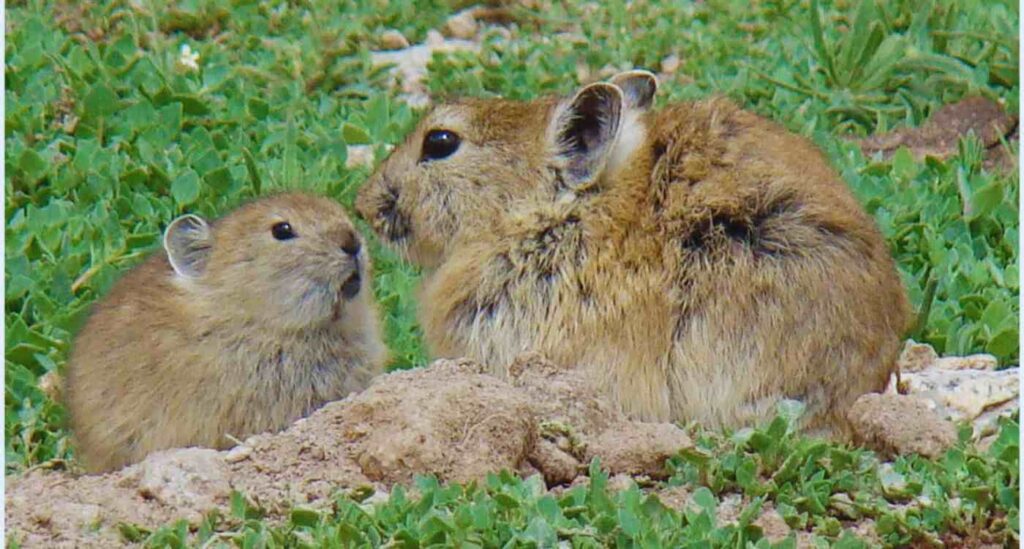

The plateau pikas have the fastest growth rate of their order. The breeding season starts in April and continues till August. The male and the female of the group create a reproductive alliance and live in a particular area. The male shows paternal care and helps the female pikas to groom the young. The adult male pika also teaches the smaller pikas to discourage a predator by emitting an alarm call. The young pikas don’t expose in the wild in the first year of birth.
Plateau pikas are very sociable animals. Usually, they live in a family of 1 male and 1 female but sometimes they also prefer a joint family, especially in desert plateau areas, where the availability of food is less. Both males and females contribute while defending their families against intruders.
Ecological Impact:
The black-lipped pikas are considered keystone species as they help in recycling the nutrients in the soil by providing food to the predators. This process helps to grow plant density in the region. The burrows of the pika also provide microhabitats for small birds and reptiles. The burrowing of the pikas helps in aerating the soil.
But the pikas are treated as a pest to the grains. They also compete with the livestock for food. The Chinese people apply an aggressive poisoning campaign to save crops from degradation and it costs the life of plateau pikas.
How Does Black-Lipped Pika Survive in Harsh Conditions?
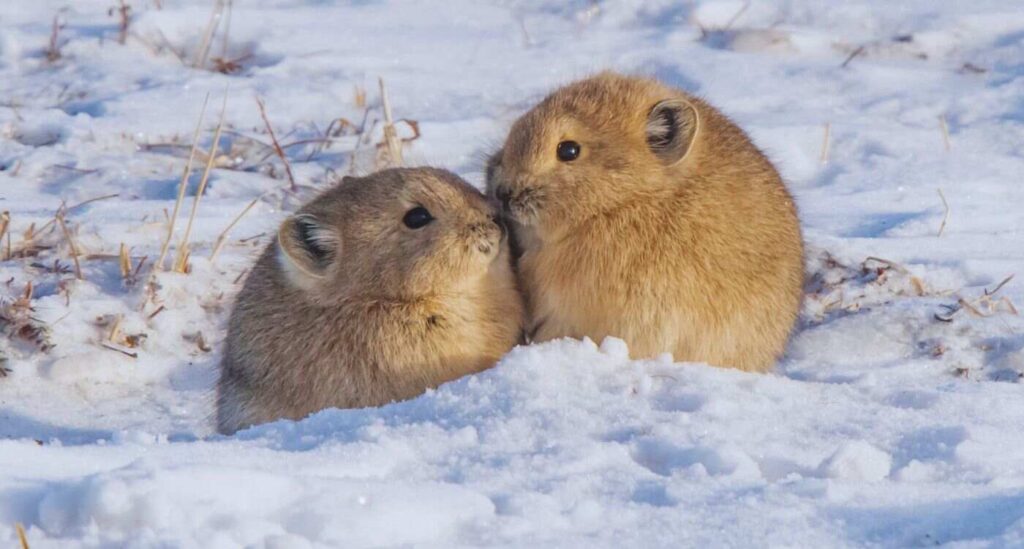

Some pikas which usually live in desert plateau regions, face extreme cold environments in winter and are a non-hibernating species. The pikas use some physiological adaptations to adjust to the harsh nature. Black-lipped pikas have high resting metabolic rates, non-shivering thermogenesis and production of leptin which acts as thermogenesis regulatory hormone. The pikas are also able to alter their adipose tissue, from white to brown, which promotes non-shivering thermogenesis. Unlike the hibernating animals, the pikas don’t rely on excess body fat to combat harsh cold conditions.
Threats:
The biggest threat to plateau pikas is humans. The pikas often compete with livestock such as Yak, Sheep, and Horses and it harms the animals as well as farmers. Thus, the farmers in China use poison to get rid of the pikas. According to researchers in the last few years, the number of black-lipped pika is decreasing.
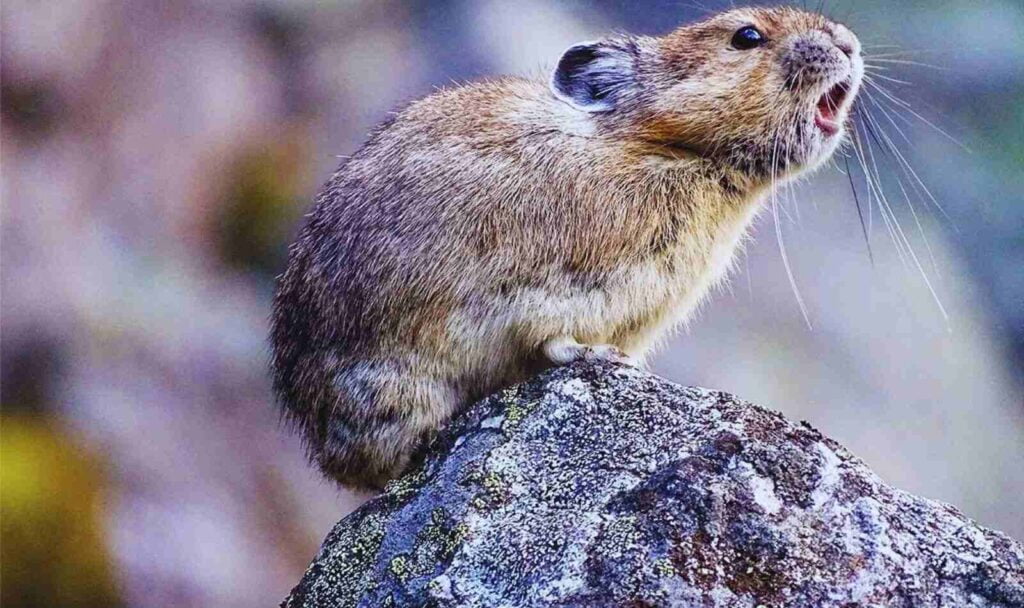

Predators:
Foxes, weasels, falcons, Asia pole cats, upland buzzards, owls and brown bears are the main predators of plateau pika. The pikas are the favourite food of the area’s brown bears.
Conservation Status:
Though the number of black-lipped pikas is decreasing, according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species it is “Least Concern”.
Conservation Efforts:
Few steps have already been taken to ensure the long-term survival of plateau pikas.
- Educate local farmers about the environmental importance of the pikas. Encourage farmers to protect crops in alternative ways so no animal life will be destroyed.
- Establish protected areas for pikas and other wildlife animals. Eg: The Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve in China.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Are plateau pika endangered?
The number of plateau pikas is decreasing over the years. But the species is listed as “Least Concern” in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Why is the plateau pika a keystone species?
The black-lipped pikas are considered keystone species as they help in recycling the nutrients in the soil by providing food to the predators. This process helps to grow plant density in the region. The burrows of the pika also provide microhabitats for small birds and reptiles.
What are the predators of plateau pika?
Foxes, weasels, falcons, Asia pole cats, upland buzzards, owls and brown bears are the main predators of plateau pika.
Is it a pika rodent?
Pikas are not rodents or are not related to rats, guinea pigs, or chinchillas. Instead, they are closely related to rabbits or hares.
Can you keep a pika as a pet?
It is not a good idea to have a pika as a pet. Pikas are wild animals and they need a certain type of conditions to survive which is very difficult to implement at home.
Are Pikas aggressive?
North Americans are more aggressive than Asian Pikas. They are very aggressive when an intruder tries to enter their burrow. The pikas are comparatively calm in their breeding season.
Also Read: Cape Rain Frogs: 8 Fascinating Facts About African Amphibian